Are you looking to optimize your website's performance but unsure if VWO is the right choice? You're in luck! We've compiled...

Quantitative Data: Definition, Pros and Cons & Analysis Techniques
Researchers rely on standardized quantitative data collection to ensure consistency and reliability, and most importantly, to allow for the objective analysis of data collected to inform conclusions and predictions.
In this article, we will see which the the most popular data collection methods, see how to analyze the information we have gathered, and we will provide you with real-world examples to make it easy.
What is Quantitative Data?
Quantitative data deals with numbers and things you can measure objectively. It reflects quantities and includes values researchers can order, count, or measure.
Such data is crucial in many fields for quantitative data analysis and applying the right data analysis methods.
For example: in product research, quantitative data examples can be about sign-up form analysis, survey results with scaled responses, and population counts.
What is The Purpose of Quantitative Data?
Numeric by nature, quantitative data serves as the backbone for high-stakes decision-making across industries. It tells stories through digits—from survey responses rated on a measurement scale to sales figures tallied at quarter-end.
Quantitative data is essential for conducting product analysis that are free from personal bias. It uses numerical values to objectively assess customer satisfaction, so it helps businesses pinpoint areas for improvement.
When they use quantitative data, companies can perform a gap analysis to bolster their operations and services.
Types of Quantitative Data
Quantitative data helps us count and measure things. It gives precise results we can analyze with numerical data (math).
- Discrete Data: This type links to things you can count. It's about whole numbers, like the number of students in a class or cars in a lot. You can't have half a student or car, so it fits with things that are countable and won’t split into smaller parts.
- Continuous Data: This kind involves measurements of any value within a range. Think about height, temperature, or time. Continuous data isn't stuck to whole numbers; it can have fractions and decimals, and show values that change smoothly without jumps.
- Categorical Data: These are groups or categories. For example, blood types A, B, AB, and O are categorical because they sort blood into distinct groups. Shirt sizes like small, medium, and large also fall under this category because they label items without using actual measurements.
- Nominal Measurement Scales: They name things without implying order. For instance, jersey numbers on a sports team tell us who is who but don't rank players by skill or position.
- Ordinal Data: Here we do have an order or rank. Grades in schools - A is higher than B - show ordinal data. We know which is better even if we don’t know how much.
- Interval Data: With intervals, the distance between values matters. Temperature scales demonstrate interval data well because the difference between degrees is the same throughout.
- Ratio Measurement Scales: These scales have all features of interval data plus a true zero point for comparison—like weight or height—allowing ratios to be formed (e.g., someone can be twice as tall as another person).
How To Collect Quantitative Data?
To collect data from your web survey questions or other types and forms, you need to have a proven system in place. These methods help you find answers to their specific research questions.
- Researchers use probability sampling to randomly choose a group of people from a larger population. This gives everyone an equal chance of being selected. They often use simple random sampling where they pick people by chance, like drawing names from a hat. Probability sampling helps get a representative sample that reflects the wider group.
- Online survey tools make it easy for people to answer questions on computers or phones. It is capable of reaching many people quickly.
- Questionnaires mailed to homes or handed out in public spaces are also common. They ask about things like habits, opinions, and experiences.
- Survey software helps collect responses which data analysts then examine for patterns and trends.
- Face-to-face interviews let researchers ask detailed questions. They record answers which are later turned into numbers for analysis.
- Phone interviews work well when meeting in person is hard. The method still allows for direct communication between the interviewer and the participant.
- Researchers sometimes use data collected by other organizations or studies. They look at open-source datasets that are free to use. It works perfectly with government records, health statistics, or education scores which already exist as numerical data.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Data
Qualitative and quantitative data serve distinct roles, each with unique strengths. Qualitative data offers nuanced understanding, while quantitative data provides measurable evidence.
Depth
Qualitative data captures the depth of human experiences and provides much more context through face-to-face interviews and open narratives. It reveals the underlying reasons behind behaviors and decisions, getting into the subtleties that statistically analyzed figures may overlook.
Such type of data is rich in details and is often presented in a tabular format to organize valuable insights.
Purpose
Quantitative data's purpose is to quantify information and generalize results from a data sample. It relies on close-ended questions to provide concrete evidence that supports predictions about future data trends and patterns.
It's essential for hypothesis testing and offering a broad overview that can be easily compared and statistically analyzed.
Use Cases
Quantitative data shines in scenarios where objectivity is key—like frequency analysis in market research or gap analysis in performance metrics. People prefer it when they present information or findings from 100s of respondents. It's indispensable in fields like finance or medicine, where precise measurements are crucial.
Qualitative data, with its descriptive richness, is invaluable in fields such as anthropology or user experience analysis, where understanding the depth of human interaction with physical objects or services is essential.
Advantages of Quantitative Data
Quantitative data analysis methods have their advantages, and that's why they are so frequently used. Let's see some of the biggest pros.
1. Objectivity in Numbers
The quantitative data collected is made to be accurate. You're comparing two products online and one has an average star rating based on thousands of users while the other relies solely on passionate testimonials. Which seems more trustworthy? That's right, numbers don't lie.
Such objectivity is especially crucial when making big decisions affecting your business or research outcomes. When you put your faith in numerical evidence, you can identify website issues proactively, and take measures in no time.
2. Scalability
Sometimes size does matter—especially when it comes to data scalability. With quantitative methods, enlarging your study from 100 to 10,000 participants is easy to do. The scalability lets businesses grow their insights alongside their operations without skipping a beat.
Beyond just piling up numbers, scaling quantitatively also means maintaining consistency throughout your analysis.
3. Easily Presentable
When you conduct quantitative data analysis, you can easily present information in front of your colleagues. You can use it on presentations, spreadsheets, etc.
- No bias dressed as fact here - number-based insights keep things clear-cut and objective.
- Growth potential? Absolutely - go ahead and scale those studies up.
- Capturing widespread trends becomes easier because generalizing large groups isn’t playing guesswork anymore—it’s a strategy powered by statistics with a precision focus.
Challenges Associated with Quantitative Data
Quantitative data analysis might look perfect on the surface, but it's not without its disadvantages. Let's see in the next few paragraphs.
1. Limits in Capturing Complexity
Quantitative data captures everything fast and gives you the numbers quickly, but sometimes it misses the nuances—the emotions, motivations, and stories behind those figures.
Sure, we can count how many people left your website after hitting the landing page (heatmaps might tell us that much), but why they bounced is a tale better told by qualitative insights.
If you're not careful, you'll make calls based on half-painted pictures.
2. Chances for Misinterpretation
Numbers can easily be twisted if not read well. You've got piles of collected data—great. But that's not all. It's how you read the data as well.
The key takeaway? Always pair stats with insights. Descriptive statistics can be both qualitative and quantitative, so it's hard not to skip one for the other.
3. Influence of Measurement Errors
Due to the numerical nature of qualitative data, a little measurement error can throw off your entire dataset. Let’s say we’re tracking user engagement through a session recording software tool.
If the results from the online surveys are not accurate (for example, a few entries weren't logged and the satisfaction rate is 92% instead of 77%), you might draw inaccurate conclusions.
Install Your First Website Feedback Form Right Now
It takes less than 5 minutes to set up your first website or app feedback form, with FullSession, and it's completely free!
- Install FullSession: Before creating a form, make sure FullSession is installed and set up on your website.
- Access Feedback Widget: Use the FullSession dashboard to access the feedback widget, which can collect varied customer insights.
- Customize the Form: Tailor your FullSession form to ask the right questions and gather the specific data you need.
- Set Collection Parameters: Define which segments of users or customer journeys you want to collect data from, ensuring relevance and precision.
- Analyze Collected Data: After data collection, use FullSession's analytical tools to study the feedback, spot trends, and make informed decisions.
Yes, it is that simple.
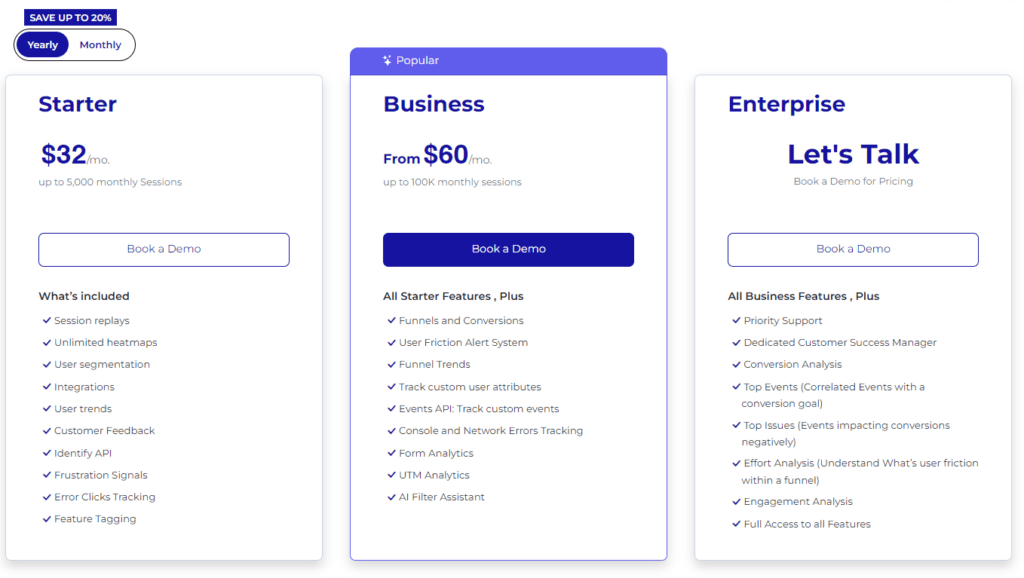
FullSession Pricing Plans
Here are more details on each plan.
- The Starter plan costs $39/month or $32/year and allows you to monitor up to 5,000 monthly sessions with up to 6 months of data storage.
- The Business plan costs $75/month or $60/year and helps you to track and analyze up to 100,000 monthly sessions with up to 12 months of data storage.
- The Enterprise plan has custom pricing and offers customizable sessions plus full access to all features.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding quantitative data types and analysis techniques is crucial for making informed decisions. Quantitative data provides valuable insights into numerical trends and patterns.
Knowing how to collect and analyze quantitative data empowers researchers and professionals to draw accurate conclusions from their findings. And if you learn how to do it with FullSession, you can easily take advantage of any situation.
FAQs About Quantitative Data
What distinguishes quantitative data from qualitative data?
Quantitative data adds real-world evidence to support statistical analysis and predictions, unlike qualitative data, which is more about depth and context to behaviors and decisions.
Why is quantitative data important in decision-making?
Quantitative data is crucial for presenting information because you can measure unbiased results. And it's very potent for scaling since you can easily measure results from 10 or 10,000 responses.
How does quantitative data contribute to market research?
When you apply quantitative data knowledge, you can easily spot news trends and identify patterns in user behavior. What's more, it's way more likely to collect many results in no time.